In the IOT in Pharma Sector, the Internet of Things (IoT) has become a disruptive force, transforming everything from supply chain management to drug development. IoT is changing how pharmaceutical organizations function by facilitating real-time data collection, improved connectivity, and automation, which guarantees increased patient safety, efficiency, and compliance.
Adoption of IOT on Pharma sector in Early Stages:
The Internet of Things (IoT) started to gain popularity in the early 2000s, but at first, technological limitations and strict regulations hampered its use in the pharmaceutical sector. IoT was mostly linked to simple sensor-based systems and radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags at this time, which were used to track inventory and guarantee supply chain traceability. These early systems addressed problems that were important to the industry, such as inventory mismanagement and medicine counterfeiting. To ensure authenticity and minimize losses from theft or spoiling, RFID technology was used, for example, to track the movement of pharmaceutical supplies. The lack of defined frameworks, restricted device compatibility, and high implementation costs made it difficult for pharmaceutical organizations to embrace IoT. Adoption was further hampered by the industry’s cautious approach to new technology, which was motivated by the necessity to comply with regulations.
Adoption of IOT on Pharma sector in Present:
Because of developments in sensor technology, cloud computing, and data analytics, IoT has emerged as a key component of pharmaceutical operations by 2025. Nowadays, IoT is integrated into many aspects of the pharmaceutical value chain, such as supply chain management, manufacturing, clinical trials, and drug development. IoT-enabled sensors give end-to-end supply chain visibility, from sourcing raw materials to product delivery, and ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) by continuously monitoring vital parameters like temperature, humidity, and pressure. Real-time product tracking via RFID tags and Internet of Things sensors minimizes delays and guarantees regulatory compliance.
Adoption of IOT on Pharma sector in Future:
IoT in the pharmaceutical sector appears to have a bright future, with notable expansion anticipated over the next ten years.It is projected that IoT will be completely incorporated into pharmaceutical operations by 2030, with connected clinical trials, intelligent production facilities, and smooth supply chains becoming standard practice. The possibilities of IoT will be further enhanced by the adoption of cutting-edge technologies like 5G, edge computing, and blockchain, which will allow for quicker data transfer, real-time analytics, and safe data management. IoT will propel the creation of fully automated, IoT-enabled smart factories that optimize production processes, cut waste, and guarantee quality by utilizing real-time data. Digital twins, which are virtual representations of physical assets, will be used in these factories to model and improve manufacturing processes.
Drivers of IoT Adoption in the Pharmaceutical Sector:
- Operational Efficiency Demand
The pharmaceutical sector is under tremendous pressure to cut expenses and boost productivity because drug research is expensive (about $2.6 billion for each new medication) and takes a long period (10–14 years). Real-time monitoring and automation are made possible by IoT, which also minimizes waste and optimizes resource allocation while lowering production downtime. Predictive maintenance powered by IoT, for instance, can reduce expenses and increase uptime by preventing equipment problems.
- Adherence to Regulations
Pharmaceutical enterprises must adhere to strict quality standards and traceability due to requirements from agencies such as the FDA and EMA. IoT ensures adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Good Distribution Practices (GDP) by offering auditable data trails and real-time monitoring. IoT sensors lower the chance of non-compliance by assisting in the maintenance of ideal conditions for biomaterials.
- Transparency in the Supply Chain
Disruptions to global supply chains, like the COVID-19 pandemic, have brought attention to the necessity of end-to-end visibility. Real-time tracking of raw materials and completed goods is made possible by IoT technologies like GPS trackers and RFID tags, which cut down on delays and guarantee product integrity. In order to combat drug counterfeiting and guarantee patient safety, this transparency is essential.
- Developments in Technology
IoT solutions are now more affordable and widely available thanks to developments in sensor technology, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. Pharmaceutical firms are now able to implement IoT at scale thanks to the development of inexpensive sensors and 5G connectivity, while AI-driven analytics increase the value of data created by IoT.
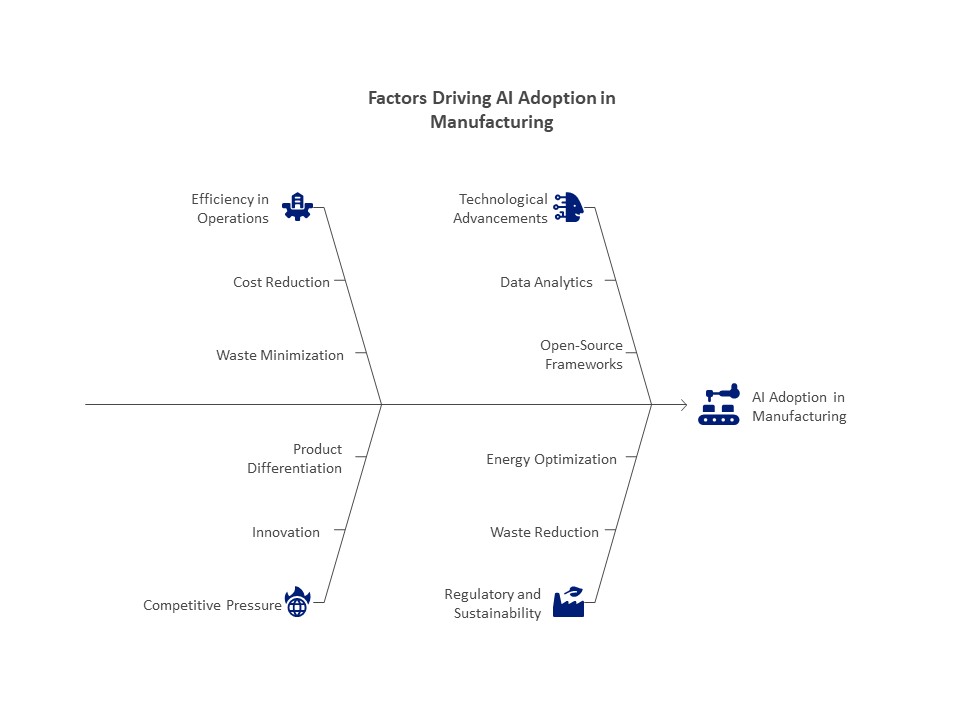
Restraints of IoT Adoption in the Pharmaceutical Sector:
- Expensive implementation fees
The upfront cost of implementing IoT infrastructure, including as sensors, connectivity options, and data analytics platforms, continues to be a major obstacle in spite of developments. It could be difficult for small and mid-sized pharmaceutical companies to defend these expenditures, especially when the returns are questionable.
- Privacy and Data Security Issues
Intellectual property and patient health information are among the sensitive data handled by the pharmaceutical sector. Because IoT devices are susceptible to hackers, there are worries about data breaches and non-compliance with regulations. Although they are necessary, strong cybersecurity measures increase the expense and complexity of IoT deployment.
- Difficulties with Regulation
Strict restrictions apply to the pharmaceutical sector, and IoT technologies must pass stringent validation to guarantee compliance. Implementation delays and cost increases may result from the absence of defined regulatory frameworks for IoT applications, such as decentralized trials and smart medicines.
- Problems with Interoperability
The variety of IoT platforms and devices makes interoperability difficult to guarantee. IoT system integration with current infrastructure can be difficult and time-consuming in the absence of established protocols.
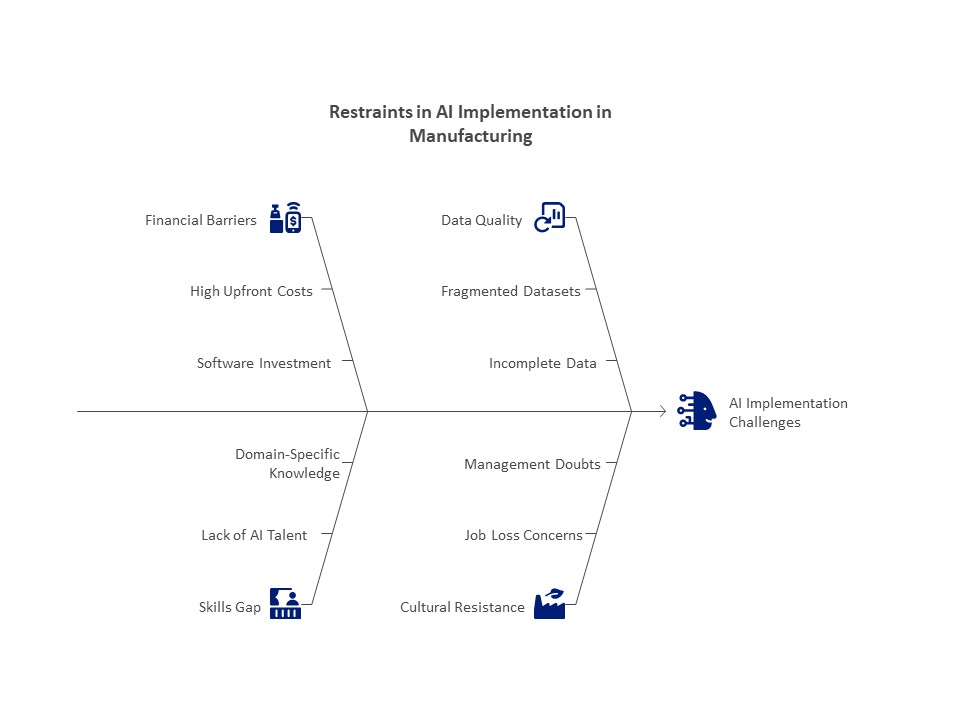
Challenges of IoT Adoption in the Pharmaceutical Sector:
- Scalability and Data Management
Large volumes of data—often in terabytes or petabytes—are produced by IoT, necessitating a strong infrastructure for analytics and storage. It can be quite difficult to manage this data while maintaining performance and scalability, especially for businesses using legacy systems.
- Risks to Cybersecurity
Cyberthreats like ransomware and data breaches have a larger attack surface when IoT devices are integrated. To protect sensitive data, pharmaceutical businesses need to put complex security processes in place, which can be resource-intensive.
- Adherence to Regulations
It’s difficult to make sure IoT systems abide by international laws like GDPR, HITECH, and HIPAA. The regulatory burden is increased by the absence of precise rules for new IoT uses, such as smart implants.
- Legacy System Integration
Numerous pharmaceutical businesses still use antiquated technologies that aren’t made to work with contemporary IoT solutions. It can be expensive and time-consuming to upgrade these systems or make sure they are compatible.
- Privacy and Ethical Issues
Concerns around consent and data protection are ethical issues brought up by the usage of IoT in patient monitoring. In a global setting with disparate privacy rules, it is crucial but difficult to ensure that patients are properly informed and give their consent for data gathering.
From simple RFID tracking in the early 2000s to a key component of contemporary operations in 2025, the Internet of Things has completely changed the pharmaceutical sector. These days, IoT promotes individualized treatment, improves supply chain transparency, and permits real-time monitoring, all of which increase patient safety and efficiency.


