Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing Sector:
In the industrial industry, artificial intelligence (AI) has become a disruptive force that is altering procedures, streamlining operations, and spurring innovation. AI is transforming the way manufacturers work, from supply chain efficiency and predictive maintenance to automating repetitive jobs. This blog examines the development of artificial intelligence (AI) in manufacturing, its present situation, its prospects for the future, and the main forces, obstacles, and difficulties influencing its uptake. This extensive analysis, which is over 5,000 words long, offers insights into how artificial intelligence is changing the manufacturing sector.
Adoption of AI in Manufacturing in Early Stages:
Long before artificial intelligence became a trendy term, technology was being incorporated into production. Early automation technologies including computer numerical control (CNC) machines and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) were used by the manufacturing industry in the 1960s and 1970s. These systems lay the groundwork for precision and efficiency but lacked the cognitive capabilities of modern AI. Limited computing power and data availability have impeded the deployment of AI in manufacturing. Real-time data processing was practically impossible, and manufacturers had to rely on fragmented datasets. The lack of advanced algorithms and scalable infrastructure meant that AI’s potential remained largely untapped.
The Revolutionary Effect of AI on Manufacturing:
Industry 4.0, the fourth industrial revolution characterized by intelligent, networked systems, is based on artificial intelligence.AI-powered predictive maintenance forecasts equipment breakdowns before they happen by analyzing sensor data using machine learning models. AI-powered computer vision systems are more accurate than human inspectors at checking products for flaws. Real-time picture analysis by these devices identifies irregularities in assembly, surface polish, or dimensions. Unlike typical robots, cobots work alongside human operators, employing AI to adapt to dynamic settings. By interacting with workers through natural language processing (NLP) and visual technologies, these robots increase worker flexibility in activities like packaging and assembly.
Adoption of AI in Manufacturing in Future:
Automation of Factories:
The idea of “lights-out” production, in which factories run with little assistance from humans, is starting to come to pass. Whole production lines, from the processing of raw materials to final assembly, will be managed by AI-driven systems. Fully automated factories are already being tested by companies such as Fanuc.
AI-Human Cooperation:
Human-AI cooperation will continue to be essential even as automation rises. AI will enhance human abilities, freeing up workers to concentrate on strategic and creative work. AI-powered augmented reality (AR) technologies will help workers navigate intricate assembly procedures.
Combining Emerging Technologies:
AI’s capacity to resolve intricate production optimization issues will be improved by quantum algorithms.Supply chains will be transparent and traceable thanks to blockchain technology and artificial intelligence. AR driven by AI will transform manufacturing maintenance and training.
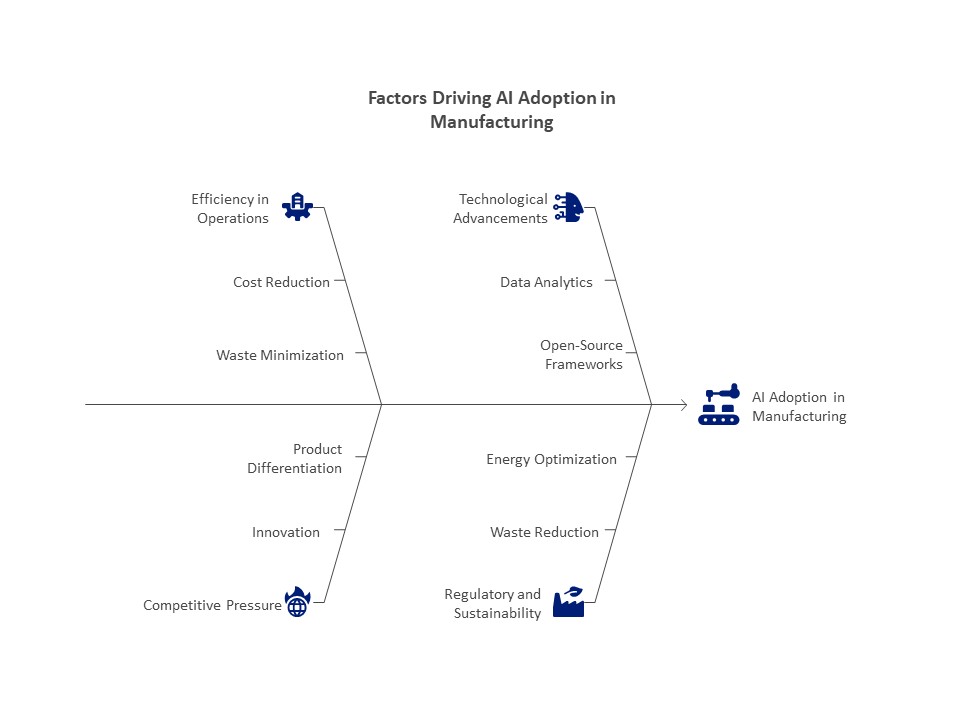
Drivers Influencing Manufacturing’s Adoption of AI:
Efficiency in Operations
AI saves a lot of money by streamlining manufacturing, cutting down on waste, and minimizing downtime. For instance, Deloitte claims that AI-driven predictive maintenance can cut maintenance expenses by as much as 30%.
Pressure from Competition
In a global market, manufacturers are under pressure to innovate and maintain their competitiveness. Businesses may set themselves apart with AI by producing goods more quickly, with better quality, and with more specialized products.
Developments in Technology
AI is becoming more widely available and efficient because to advancements in data analytics, processing power, and AI algorithms. Entry hurdles have decreased due to the availability of open-source AI frameworks such as PyTorch and TensorFlow.
Regulatory and Sustainability Objectives:
Manufacturers are being pushed to use AI for waste reduction and energy optimization by government regulations and consumer demand for sustainable practices.
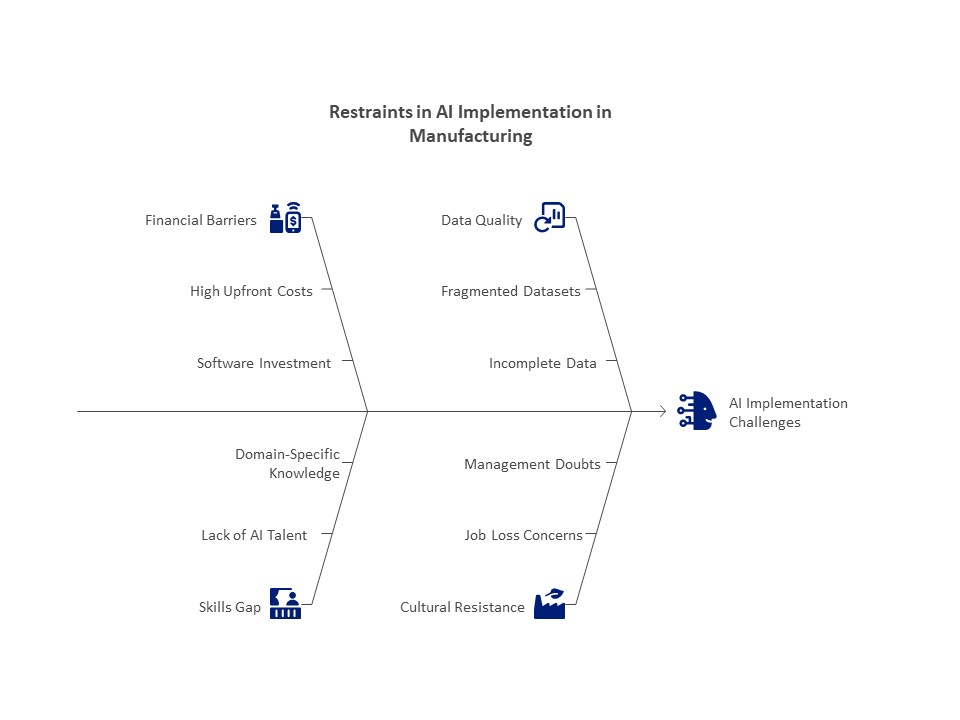
Restraints on the Use of AI in Manufacturing:
Expensive upfront expenses
AI implementation necessitates a large infrastructural, software, and hardware investment. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) frequently find it difficult to cover these up-front expenses.
Insufficiently Skilled Personnel
Implementing AI requires domain-specific knowledge, machine learning skills, and data science competence. One major obstacle is the worldwide lack of AI talent.
Availability and Quality of Data
AI models require well-structured, high-quality data. The usefulness of AI is nevertheless limited by the fact that many manufacturers still work with fragmented or incomplete datasets.
Opposition to Change
The implementation of AI may be slowed by organizational cultural opposition, especially among traditional manufacturers. Employees might worry about losing their jobs, and management might doubt AI’s return on investment.
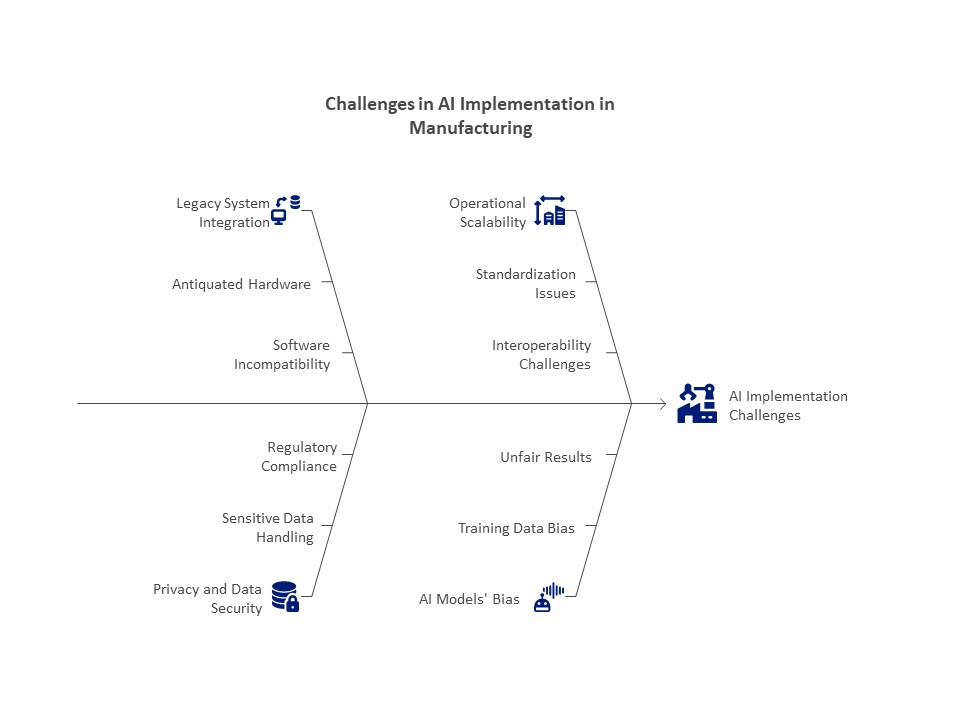
Challenges in Implementing AI in Manufacturing:
Legacy System Integration
Numerous manufacturing plants still use antiquated hardware and software that cannot be used with contemporary AI systems. These systems require a lot of effort and money to retrofit.
Privacy and Data Security
From customer information to production metrics, manufacturing produces enormous volumes of sensitive data. A major difficulty is ensuring data security and regulatory compliance.
Operational Scalability
AI may be effective in pilot projects, but it is difficult to scale across numerous factories or international supply chains. Standardization and interoperability continue to be major obstacles.
AI Models’ Bias
Biases from training data may be inherited by AI models, producing unfair results or erroneous predictions. Biased quality control models, for instance, could fail to notice some flaws.
AI is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by promoting creativity, quality, and efficiency. AI has advanced significantly since its modest origins with expert systems and is now used to power smart industries. In the future, new opportunities will be opened by combining AI with cutting-edge technologies like blockchain and quantum computing. To fully fulfill AI’s promise, however, issues including high costs, data quality, and labor upskilling must be resolved.
Leading the industry into a new era of sustainability and productivity will be manufacturers who deliberately adopt AI while striking a balance between ethical issues and technological breakthroughs. AI’s influence on manufacturing will only increase as it develops further, influencing a future in which human-AI cooperation and smart factories redefine what is feasible.


