With the opportunity to outsource different IT Infrastructure and operational responsibilities to specialized providers, the managed services market has become a vital component of contemporary business operations. By using outside expertise to manage complex systems, improve efficiency, and spur innovation, this strategy enables companies to concentrate on their core strengths. From the early days of simple IT outsourcing to the complex, cloud-driven systems of today, the development of managed services reflects wider technological and economic changes.
Managed Services Market in the Past:
Early IT outsourcing, which started to gain popularity in the late 20th century, is where the idea of managed services got its start. Around this time, companies began to realize that outsourcing non-core tasks to outside vendors would help them streamline operations and cut expenses. Basic IT support, including helpdesk services, software upgrades, and hardware maintenance, was the extent of managed services at first. Businesses looked to contract out routine work to outside vendors that could give dependable assistance at a cheaper cost than internal teams. The market was defined by strict service agreements and long-term contracts that had little room for adaptation to shifting business requirements. Cost cutting was the main objective, frequently at the price of creativity or personalization.
Managed Services Market in the Present:
Businesses of all sizes and sectors are served by the growing managed services market of today. The range of managed services has changed due to the widespread use of cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT). A wide range of services are provided by contemporary MSPs, such as application management, cybersecurity, data analytics, and managed cloud services. While major organizations utilize managed services to optimize complex, hybrid IT environments, small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) rely on MSPs to access enterprise-grade technology without having to make a sizable capital investment.In order to guarantee smooth connectivity and productivity, the growing popularity of remote work has also increased demand for managed network and collaboration solutions. The market for managed services is marked by fierce rivalry and market consolidation. Niche MSPs, consulting organizations, and large technology corporations all target different market groups. MSPs and cloud providers like Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) frequently form partnerships that allow the providers to create customized solutions.
The Managed Services Market in the Future:
Rapid technology advancements and changing business needs are expected to shape the managed services market’s future. MSPs will be essential in fostering innovation as businesses continue to embrace digital transformation. Service delivery will be redefined by the combination of automation, AI, and machine learning (ML), which will enable providers to predict problems, maximize resources, and give individualized experiences. For instance, MSPs will be able to anticipate system failures before they happen thanks to AI-driven analytics, and mundane chores like patch management and backups will be made easier by automation.Managed services will see new opportunities as a result of emerging technologies like 5G, edge computing, and quantum computing. Data processing may undergo a revolution thanks to quantum computing, which is why MSPs are providing specific services for managing quantum infrastructure.
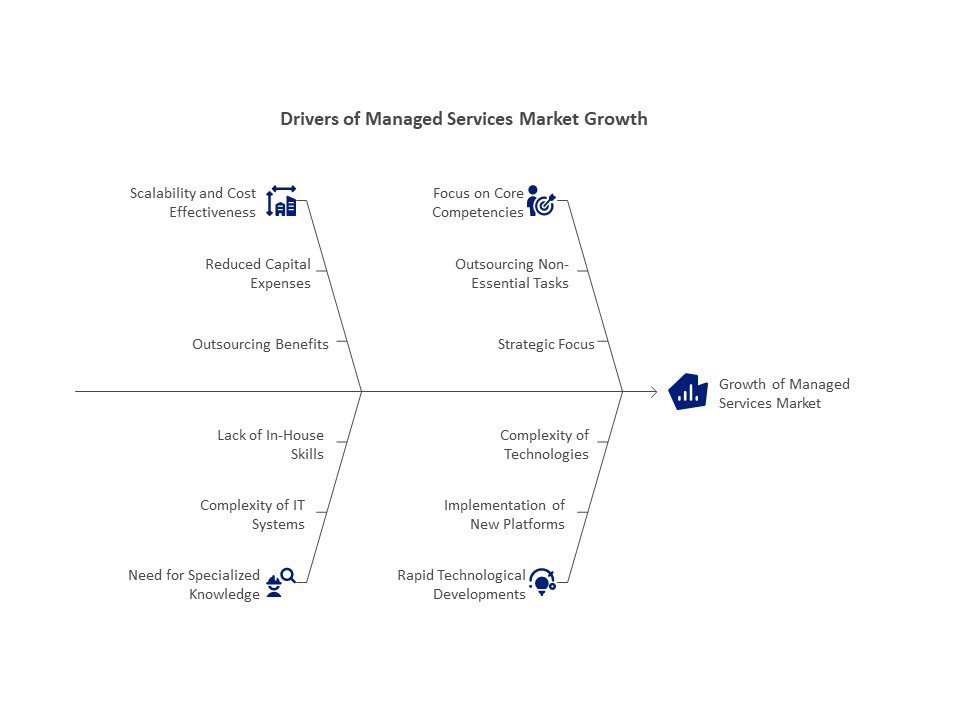
Market Drivers for Managed Services:
Scalability and Cost Effectiveness
The promise of cost effectiveness is one of the main factors propelling the managed services market. Organizations can cut capital expenses on gear, software, and in-house expertise by outsourcing business and IT functions.
The need for specialized knowledge
Many firms are unable to maintain in-house specialist skills due to the growing complexity of IT systems.
Pay attention to your core competencies.
By assigning non-essential tasks to outside suppliers, managed services enable companies to concentrate on their primary strengths.
Quick Developments in Technology
One of the main factors propelling the managed services industry is the rate of technological advancement. To be competitive, businesses need to implement new platforms and tools, yet the intricacy of these technologies can be daunting.
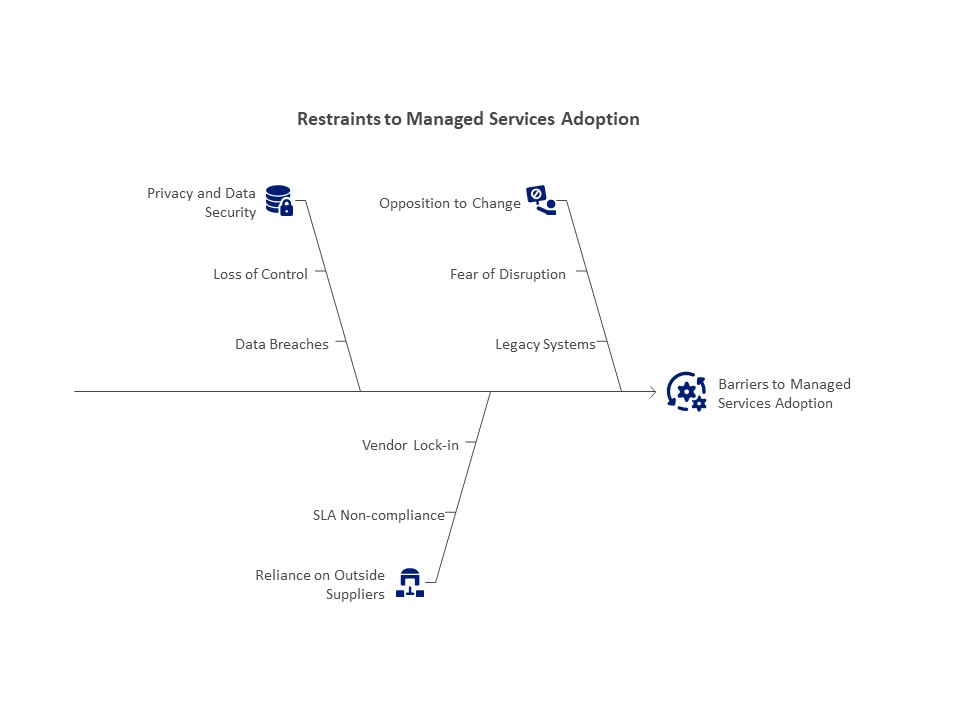
Restraints of the Managed Services Market:
Privacy and Data Security Issues
Data security and privacy issues continue to be major barriers in spite of the advantages. Companies that provide third-party suppliers access to sensitive data run the risk of losing control, data breaches, and noncompliance.
Reliance on Outside Suppliers
Dependency on MSPs can hinder an organization’s capacity to handle its own IT infrastructure. If a provider doesn’t meet SLAs or if a company needs to switch vendors, this could be an issue. Another issue is vendor lock-in, which occurs when businesses are obligated to a provider’s ecosystem and can ultimately limit flexibility and raise prices.
Opposition to Change
One significant barrier is organizational reluctance to change. Some companies are reluctant to use managed services because they fear disruption or losing control, especially those with legacy systems or traditional attitudes. Clear value demonstration and overcoming organizational culture barriers are necessary to persuade stakeholders to support outsourcing.
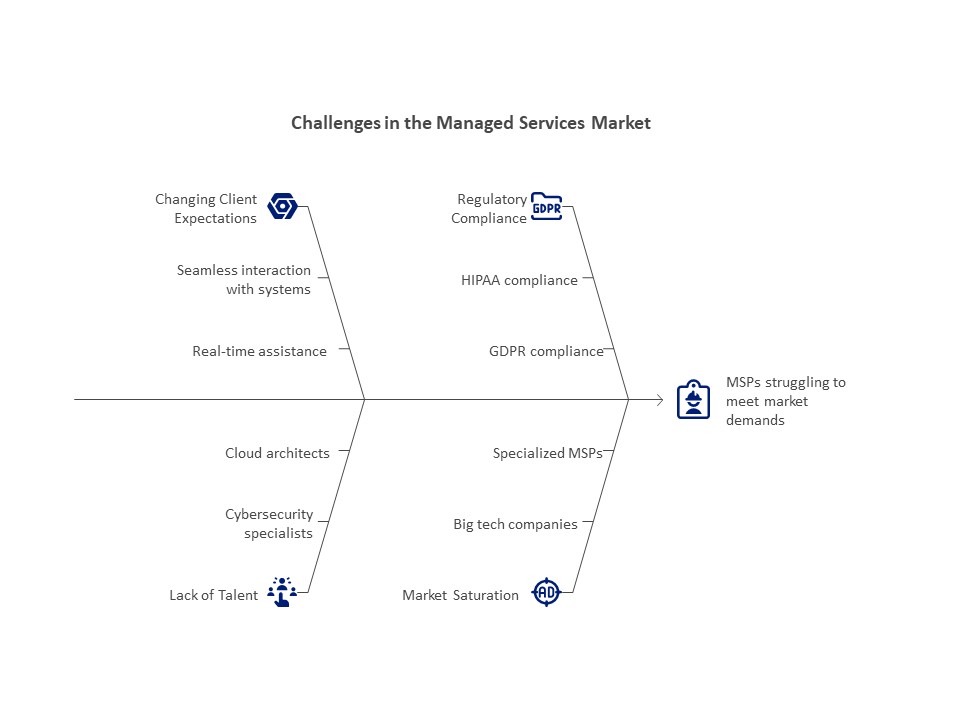
Challenges in the Managed Services Market:
Fulfilling Changing Client Expectations
Businesses are expecting more from MSPs as they become more tech-savvy. Customers want seamless interaction with current systems, real-time assistance, and tailored solutions. MSPs must make investments in cutting-edge technology, qualified personnel, and strong customer service frameworks in order to meet these demands. Client attrition and reputational harm may arise from a failure to perform.
Lack of Talent
The market for managed services is highly dependent on qualified workers, yet a major obstacle is the lack of talent. It is challenging for MSPs to find and keep top talent because there is a huge demand for specialists in fields like cybersecurity, cloud architecture, and artificial intelligence. To create a competent staff, providers must make training and development investments, which might put a pressure on their resources.
Adherence to Regulations
It’s never easy to navigate the complicated world of regulatory compliance. MSPs are required to make sure that their services comply with industry-specific laws, such as HIPAA for healthcare or GDPR for data privacy.
Market Saturation and Competition
There are many companies fighting for market share in the fiercely competitive managed services sector. To set themselves apart, big tech companies, specialized MSPs, and newcomers are always coming up with fresh ideas. It is difficult for suppliers to stand apart due to this saturation, especially for smaller businesses with fewer resources. Overcoming this obstacle requires developing a distinctive value proposition and cultivating client connections.
The industry for managed services has advanced significantly from its inception as a simple IT outsourcing model. Due to the demands of cost effectiveness, specialized knowledge, and digital transformation, it is now a vibrant and essential component of the global corporate environment.


